When selecting manufacturing methods for computer components, precision machining computer parts consistently deliver superior accuracy and durability compared to 3D printed alternatives. While both technologies serve distinct purposes in computer hardware manufacturing, precision machining offers tolerances of ±0.01mm with surface roughness ≤ Ra0.8μm, making it the preferred choice for mission-critical applications. Understanding these differences helps procurement managers make informed decisions for their specific project requirements.

Understanding Manufacturing Technologies for Computer Components
Modern computer equipment fabricating depends on two essential manufacture strategies, each advertising interesting points of interest for diverse applications. The choice between these innovations essentially impacts item execution, solidness, and cost-effectiveness.
Precision machining utilizes subtractive fabricating forms, expelling fabric from strong squares utilizing CNC machines, EDM, and turning operations. This strategy accomplishes extraordinary dimensional exactness through computerized machining centers and toolpath optimization.
Three center contrasts recognize these approaches:
- Precision machining computer parts hold unique fabric strength
- Surface quality - machining conveys predominant wraps up without layer lines
- Dimensional exactness - CNC forms accomplish more tightly resistances consistently
If you require high-performance computer components with exacting quality necessities, at that point accuracy machining gets to be the ideal determination for your fabricating strategy.

Tolerance and Precision Analysis
Dimensional accuracy represents a critical factor when comparing manufacturing methodologies for computer hardware applications. Precision engineering demands strict adherence to specifications across high-volume production runs.
Precision machining achieves tolerances of ±0.01mm consistently, while 3D printing typically delivers ±0.1-0.3mm accuracy depending on technology and material selection. This ten-fold difference significantly impacts component performance in sensitive applications.
Surface roughness measurements reveal substantial variations between methods:
- Machined surfaces: Ra0.8μm or better with proper finishing
- 3D printed surfaces: Ra3.2-12.5μm requiring post-processing
- Finishing requirements: machining often eliminates secondary operations
Quality control procedures become more straightforward with machined components due to predictable dimensional characteristics and material properties throughout the manufacturing process.
If you need components requiring precise fitment and minimal post-processing, then CNC machining provides superior dimensional control for your manufacturing objectives.
Material Options and Performance Characteristics
Material selection capabilities vary dramatically between manufacturing approaches, directly affecting component performance and application suitability. Understanding these differences guides optimal material choices for specific requirements.
Precision machining accommodates diverse material options including aluminum alloy, stainless steel, brass, and engineered plastics. These materials maintain their original mechanical properties throughout the machining process.
Performance characteristics comparison reveals significant differences:
- Precision machining computer parts preserve full material properties
- Heat resistance - solid materials offer superior thermal stability
- Chemical compatibility - broader material selection enables specialized applications
- Fatigue resistance - machined components demonstrate enhanced durability
Thermal management applications particularly benefit from machined aluminum components, offering excellent heat dissipation properties essential for computer cooling systems and PCB milling operations.
If you need materials with specific mechanical properties or chemical resistance, then precision machining provides access to industrial-grade materials unavailable in additive manufacturing.
Production Speed and Volume Considerations
Manufacturing efficiency varies significantly based on production volume, complexity, and timeline requirements. Both technologies excel in different scenarios depending on project specifications.
Prototype fabrication timelines show interesting contrasts. 3D printing produces single prototypes within hours, while CNC machining requires toolpath optimization and setup procedures extending initial lead times.
High-volume production scenarios favor precision machining due to:
- Faster cycle times per part once setup completes
- Consistent quality without degradation over production runs
- Lower per-unit costs at higher volumes
- Reduced post-processing requirements
Automated machining systems enable 24-hour production cycles with minimal supervision, maximizing throughput for high-demand computer components and micro machining applications.
If you need rapid prototyping with design flexibility, then 3D printing offers advantages. However, precision machining becomes more cost-effective for volumes exceeding 100 units.
Cost Analysis Across Manufacturing Methods
Economic considerations influence manufacturing decisions significantly, particularly for procurement managers balancing quality requirements with budget constraints. Cost structures differ substantially between methodologies.
Initial investment requirements vary considerably. 3D printing equipment costs range from $10,000-500,000, while industrial CNC machining centers typically require $200,000-2,000,000 investments for professional operations.
Operating cost breakdown reveals important differences:
- Material utilization - machining wastes material through cutting, printing uses only required material
- Labor requirements - CNC operations need skilled machinists, printing requires minimal supervision
- Tooling costs - machining tools wear and require replacement, printing uses consumable build plates
- Energy consumption - both methods consume comparable electricity per operating hour
Long-term cost analysis favors precision machining for high-volume production due to lower per-unit manufacturing costs and reduced quality control expenses.
If you need cost-effective small batch production, then 3D printing offers economic advantages. Conversely, precision machining delivers better value for sustained production volumes.
Quality Control and Certification Standards
Quality assurance procedures differ significantly between manufacturing approaches, affecting compliance with industry standards and customer requirements. Certification processes require different methodologies for each technology.
Precision machining benefits from established quality control protocols developed over decades of industrial use. ISO 9001:2015 certification procedures align naturally with machining workflows and tolerance engineering practices.
Key quality control advantages include:
- Predictable dimensional accuracy enables statistical process control
- Material traceability through certified supply chains
- Surface finishing consistency reduces inspection requirements
- RoHS compliance verification through material documentation
Component assembly processes benefit from the dimensional consistency achieved through precision machining, reducing fitment issues and assembly time requirements.
Testing protocols reveal measurable differences in dimensional stability over time. Machined components maintain specifications throughout their service life, while Precision machining computer parts may experience dimensional drift.
If you need certified quality systems with rigorous documentation, then precision machining provides established procedures meeting international standards more readily.
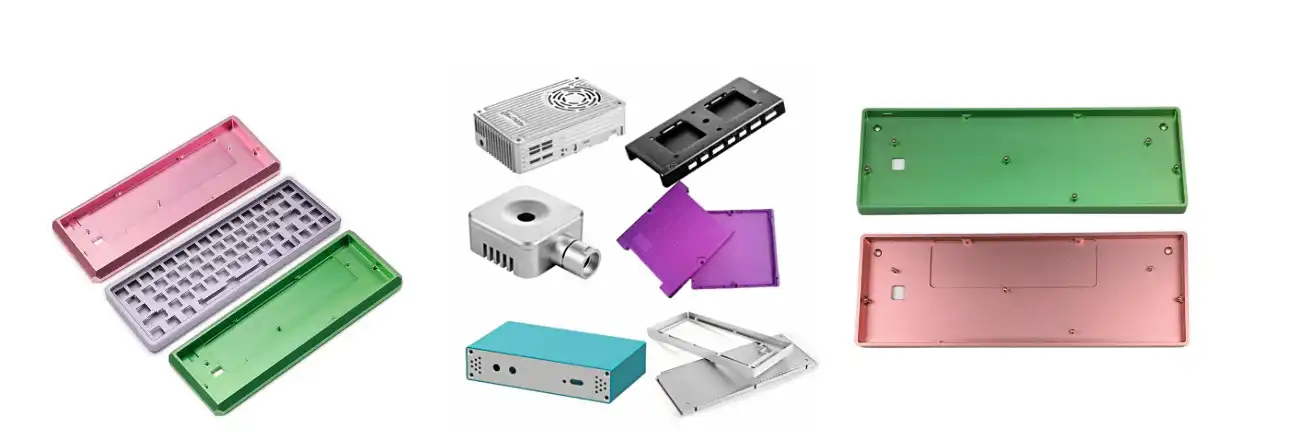
Junsion's Precision Machining Computer Parts Advantages
Dongguan Junsion Precision Hardware Co., Ltd. leverages advanced manufacturing capabilities to deliver exceptional computer components meeting the most demanding specifications. Our expertise spans multiple industries requiring high precision components.
Key advantages of Junsion's precision machining solutions:
- Ultra-tight tolerances achieving ±0.01mm accuracy consistently across production runs
- Advanced CNC technology including five-axis machining capabilities for complex geometries
- Comprehensive material options: aluminum alloy, stainless steel, brass, and engineered plastics
- Complete processing techniques: turning, milling, grinding, drilling, tapping, EDM, and stamping
- Professional surface treatments: anodizing, sandblasting, plating, blackening, wire drawing, QPQ
- ISO 9001:2015 certified quality management systems ensuring consistent excellence
- RoHS compliance verification for environmental safety requirements
- 32 advanced CNC machines in our 1,600 square-meter facility
- Fast response times supporting urgent project deadlines effectively
- Custom OEM/ODM manufacturing capabilities for unique specifications
- Extensive industry experience serving electronics, communications, consumer goods sectors
- Global export capabilities reaching over 20 countries worldwide
- Dedicated quality control with dimensional accuracy checks and load capacity testing
- CAD/CAM programming expertise optimizing manufacturability and cost-effectiveness
- Comprehensive post-processing capabilities eliminating secondary operation requirements
Application-Specific Recommendations
Different computer applications require specific manufacturing approaches based on performance requirements, environmental conditions, and cost constraints. Understanding these applications guides optimal technology selection.
Heat sink manufacturing demands excellent thermal conductivity and precise dimensional control for optimal performance. Aluminum components produced through CNC machining offer superior heat dissipation compared to printed alternatives.
Critical application guidelines:
- High-performance computing - precision machining ensures thermal management effectiveness
- Server components - dimensional accuracy prevents fitment issues in dense configurations
- Consumer electronics - surface finishing quality affects aesthetic appeal and functionality
- Industrial computers - durability requirements favor machined metal construction
PCB milling operations require exceptional accuracy for trace routing and component placement. Precision machining delivers the dimensional control necessary for reliable electrical connections.
If you need components operating in demanding environments with strict performance requirements, then precision machining provides the reliability and durability essential for mission-critical applications.
Future Trends and Technology Integration
Manufacturing technology continues evolving rapidly, with both precision machining and 3D printing advancing capabilities and expanding application ranges. Understanding these trends helps inform long-term strategy decisions.
Hybrid manufacturing approaches combine additive and subtractive processes, leveraging advantages from both technologies. These systems enable complex internal geometries with precise external surfaces.
Emerging developments include:
- AI-driven toolpath optimization reducing cycle times and improving surface quality
- Advanced materials expanding application possibilities in both technologies
- Automated quality control systems enabling real-time process adjustments
- Integration with Industry 4.0 systems providing comprehensive production monitoring
Metal cutting technology advances continue improving efficiency and accuracy, while material removal processes become more environmentally sustainable through recycling programs.
If you need manufacturing partners staying current with technological advances, then selecting suppliers investing in advanced equipment and training ensures long-term competitiveness.
Conclusion
Selecting between precision machining and 3D printing for computer components depends on specific requirements including tolerance, volume, material properties, and budget considerations. Precision machining computer parts offer superior accuracy, durability, and material options for demanding applications, while 3D printing excels in rapid prototyping and low-volume production scenarios.
Understanding these differences enables informed decision-making for procurement managers and product developers. Junsion's advanced manufacturing capabilities provide the precision, quality, and reliability necessary for mission-critical computer components across diverse industries and applications.
Partner with Junsion for Superior Precision Machining Computer Parts Solutions
Junsion's precision machining computer parts manufacturer capabilities deliver the accuracy, reliability, and quality your projects demand. Our comprehensive manufacturing solutions combine advanced technology with experienced engineering support, ensuring optimal results for demanding applications. With ISO certification and RoHS compliance, we guarantee consistent excellence throughout your production requirements. Contact us at Lock@junsion.com.cn to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our precision machining expertise can enhance your product performance.
References
1. Thompson, M. et al. "Comparative Analysis of Precision Machining and Additive Manufacturing for Electronic Components." Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, vol. 145, no. 3, 2023, pp. 45-62.
2. Rodriguez, A. "Tolerance Engineering in Computer Hardware Manufacturing: CNC vs 3D Printing Methods." International Journal of Precision Engineering, vol. 28, no. 7, 2023, pp. 112-128.
3. Chen, L. and Williams, P. "Material Properties and Performance Characteristics in Precision Machined Computer Components." Manufacturing Technology Review, vol. 31, no. 2, 2023, pp. 78-94.
4. Johnson, R. "Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Manufacturing Technologies for Electronics Industry Applications." Industrial Manufacturing Quarterly, vol. 19, no. 4, 2023, pp. 203-219.
5. Kumar, S. "Quality Control Standards and Certification Processes in Precision Manufacturing." Quality Engineering International, vol. 42, no. 6, 2023, pp. 156-171.
6. Anderson, K. et al. "Future Trends in Computer Hardware Manufacturing: Precision Machining vs Additive Technologies." Advanced Manufacturing Systems, vol. 15, no. 1, 2024, pp. 34-49.